USD - US Dollar
Currency
- USD - US Dollar
- EUR - Euro
- GBP - Pound Sterling
- AUD - Australian Dollar
- CAD - Canadian Dollar
- JPY - Japanese Yen
- HKD - Hong Kong Dollar
- TWD - Taiwan dollar
- CHF - Swiss Franc
- CZK - Czech Koruna
- DKK - Danish Krone
- HUF - Hungarian Forint
- ILS - New Israeli Shekel
- MXN - Mexican Peso
- NOK - Norwegian Krone
- NZD - Zealand Dollar
- PHP - Philippine Peso
- PLN - Polish Zloty
- SEK - Swedish Krona
- SGD - Singapore Dollar
- THB - Thai Baht
|
Shopping Cart
Search
FTTX PON Solutions
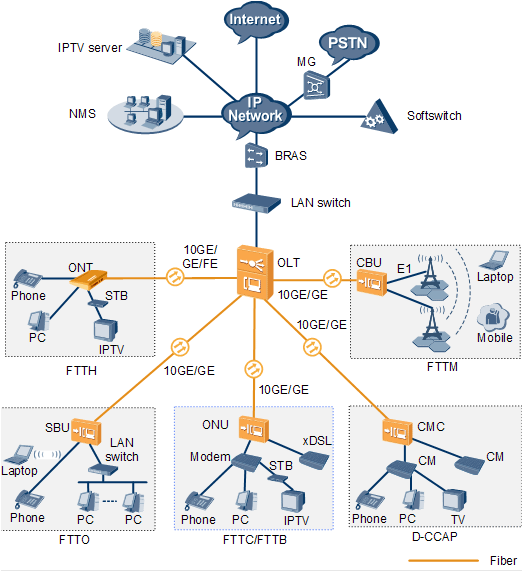
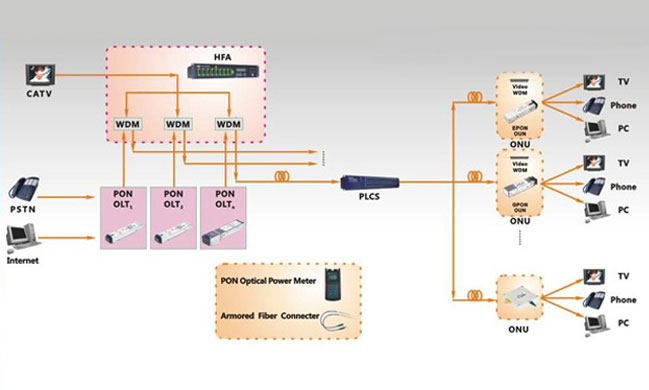
- FTTx refers to the access networking mode that uses optical fiber for the access layer network, so that the optical fiber is close to the user or even directly connected to the user. The optical fiber access network uses optical fiber as the transmission medium. It has the advantages of large transmission capacity, high transmission quality, high reliability, long transmission distance, and anti-electromagnetic interference. It has been widely used in different fiber access scenarios, including four common scenarios. : FTTH (fiber to the home), FTTB (fiber to the building), FTTC (fiber to the roadside), and FTTO (fiber to the office)
- Among all known FTTx implementation technologies, Passive Optical Network (PON) technology uses optical fiber as the transmission medium, which has the characteristics of high access bandwidth and full passive optical transmission. It is used to manage operation and maintenance, bandwidth performance, Comprehensive service provision, bandwidth allocation strategy, networking flexibility, construction cost, etc. have obvious advantages over other optical access technologies.
- FTTx is divided into three categories in the design of the transmission layer, namely duplex fiber bidirectional loop, simplex fiber bidirectional loop and triplex single fiber tridirectional loop. The duplex loop uses two optical fiber connections between the OLT end and the ONU end. One path is Downstream, and the signal is from the OLT end to the ONU end. The other path is Upstream, and the signal is from the ONU end to the OLT end. The simplex fiber loop is also called Bidirectional, or BIDI for short. This solution uses only one optical fiber to connect the OLT end and the ONU end, and uses the WDM method to transmit upstream and downstream signals with optical signals of different wavelengths, respectively. This single-fiber circuit using WDM transmission can reduce the optical fiber usage by half compared to the Duplex circuit, which can reduce the cost of the ONU user end. However, when using the single-fiber method, a splitting and combining unit must be introduced into the optical transceiver module, the architecture is a little more complicated than the optical transceiver module using the dual-fiber method. The BIDI uplink signal is selected for laser transmission in the 1260nm to 1360nm band, and the downlink uses the 1480nm to 1580 nm band. In a dual-fiber loop, signals are transmitted using the 1310nm band both upstream and downstream.
Related products for FTTX PON Solutions







































